If you’d prefer to listen to this as an audio essay at The Natural Curiosity Project, please click here.
I want to start this new year with a question.
Do the actions of a single individual matter?
If you subscribe to the fundamental tenets of negativism, pessimism, resignation, and snark, the answer to that question is decidedly ‘no.’ But let’s reconsider that.
I’m Steve Shepard with the NCP. Welcome. As a university undergrad, I studied two completely unrelated fields, Spanish and marine biology. Both were equally important to me, and both appealed to me as possible career vectors, in spite of the fact that I had no idea what I wanted to with the rest of my life. I graduated, wandered a bit, became a certified SCUBA diver, then a certified SCUBA instructor, then an owner in a diving business in the San Francisco Bay Area.

After five years of full-time diving I switched gears, married Sabine, joined the telecom industry, and had kids. I stayed with the telephone company for eleven years, then left California to join a Vermont-based consulting firm for ten years. I left them in 2000 to start my own company, where I wrote books, taught technology programs, delivered keynotes, wrote, directed and produced audio and video programs, and traveled nonstop to more than 100 countries over the course of 25 years, at which point, with the urging of the COVID lockdown, I decided to retire, having accumulated four million miles on United and a million points each with Marriott and Hilton. It was time.
To restate the obvious, I studied Spanish and biology in school, but spent my career in the world of bit-weenies and propellerheads. The funny thing is that my Spanish studies served me extremely well during my career, making it possible for me to write and teach technical training programs and deliver keynotes all over the world in Spanish. And marine biology? I never stopped diving, and I stayed connected to my biology roots. In my mind, that world is never far away.
I continue to write; I just published my 106th book, and my Podcast, The Natural Curiosity Project, just hit 300 episodes.
My newest novel, “The Sound of Life,” is a sequel to my first novel, “Inca Gold, Spanish Blood,” which was released in 2016. That first book centered around the search for a priceless treasure, and bounced back and forth between the 16th century and modern day. “The Sound of Life” builds on that, but as I worked the story arc, my passion for marine biology began to heat up again, and combined with my work as a wildlife sound recordist and my interest in bioacoustics, the story hit me like a lightning bolt. I’m proud of the book, and I think you’ll enjoy it. But, you’d be right to ask me a question right about now: What does all this have to do with the question I asked at the beginning of this essay: Do the actions of a single individual matter? Yes—they absolutely do. From my own personal experience, they matter immensely.
We’ve all had heroes in our lives. I’m not talking about the kind that appeared between the covers of DC and Marvel comics when we were kids, or who have made it onto the big screen today. I’m talking about real people, who did real things, and who, in the process, created real change by flipping the status quo on its complacent head. I’m talking about people like Rosa Parks. Jane Goodall. David Attenborough. Greta Thunberg. Barack Obama. Want more? Sure. Jacques Cousteau. James Cameron. Malala Yousafzai. Taylor Swift. The unknown man who stood in front of the tank in Tiananmen Square in 1989 with a grocery bag in his arms. The person who tore the first stone out of the Berlin Wall that same year.
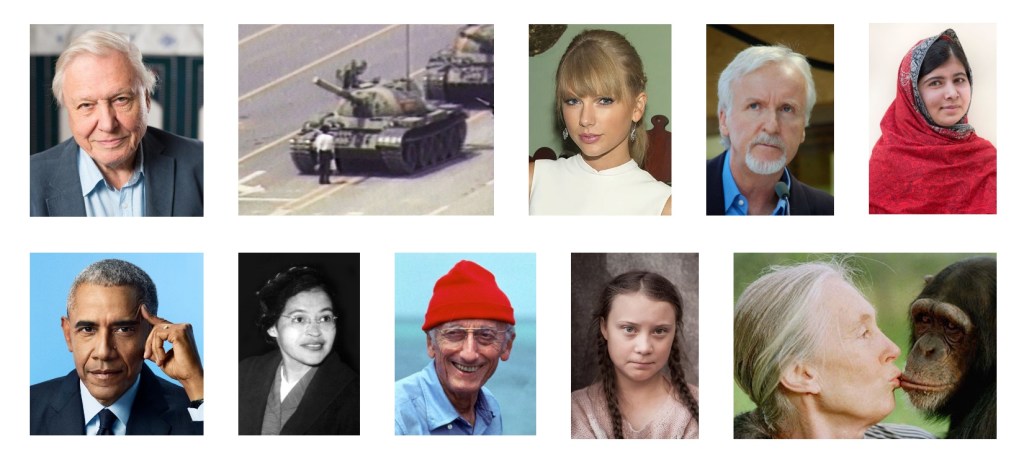

These are the individuals who come to mind for me, people who inspired me to be more, to do more, to demand more, to think beyond the confines of my own mind, to be there for others, to be less selfish, to believe that every kind act is repaid a hundred times over. Each of those individuals changed my own life as well as the lives of thousands of other people. But let’s be clear about one thing. None of them—not a single one—created change by telling us what to do. They created change by showing us what to do. They shared their beliefs and motivated change through their own actions, not by waving signs and hanging banners. They led the charge. They led. They were leaders. They demonstrated what leadership is supposed to look like.
Here’s a quote for you that I love:
“Recognize that every out-front maneuver you make is going to be lonely and a little bit frightening. If you’re entirely comfortable, you’re not far enough ahead to do any good. That warm sense of everything going well is nothing more than the body temperature at the center of the herd.”
You can’t lead from the center of the herd, which is why I learned the power of righteous indignation, not by looking it up in the dictionary or reading about it, but through the bravery of Rosa Parks and other people like her. It’s why I became an ardent conservationist and environmentalist, not because it was trendy, but because Jacques Cousteau, Jane Goodall, David Attenborough, Greta Thunberg, and many others like them showed me what we stood to lose if I and others like me didn’t take a stand. I became a wildlife sound recordist and a passionate advocate for wild places and the creatures that live there because Bernie Krause, Gordon Hempton, Melissa Pons and other recordists showed me how impoverished the planet would be if the voices of the natural world were to be silenced forever. I don’t ever want my grandchildren to ask me what a magpie sounded like. Or a tree frog. Or a humpback whale. The past tense has no place here.
And writing? My writing gets better every time I read a book. I learned long ago that skilled authors wield a power that I call lexemancy, the singular magic of language. In a well-written book, authors turn lead into gold, transmuting ideas into words, and words into breathtaking, inspiring experiences for those who read them.
Each of these people, these individuals, have inspired others. When they started, no one knew who Rosa Parks or Greta Thunberg were. Cousteau was an officer in the French Navy with a passion for the sea; Attenborough was a radio broadcaster; and Jane Goodall was a wet-behind-the-ears anthropology novice who took a chance and followed a passion. And just look what their individual passions and advocacy have accomplished—individuals all.
So: Do the actions of a single individual matter? Yes, they do. In fact, the actions of a single individual are the ONLY thing that matters.
Do your actions matter? More than you will ever know.